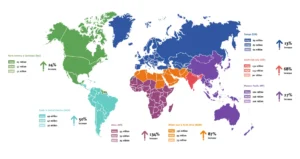
With the rise in cases of diabetes globally every year, many people may wonder ‘Is keto diet good for diabetes?’ Did you know that there are 540 million people worldwide with diabetes? And this is expected to increase to 643 million by 20307. Look at the map below by the International Diabetes Federation and you can see how alarming the increase is set to be. Currently, 10.5% of the population have diabetes and half of them don’t even know they have it. In Australasia, we are predicted to have an increase in 27% of diabetic cases, North America, 24%, Europe, 13% by 2030.
Image Source: IDF-Global Diabetes Statistics7(03/06/24)
Is Keto Diet The Answer To Managing Blood Sugar Levels?
If you’re diabetic you probably would have wondered at some point whether the keto diet is good for you. You probably would have come across some low carb snacks as options and may have even seen keto snacks on the market or seen keto diet on social media. But is the keto diet suitable for diabetics?
To answer this, we need first to understand how diabetes works, how the ketogenic diet works, how sugars, carbs, protein and fats play a role in diabetes and how they can affect your blood sugar levels. We’ll explore whether keto foods and snacks are a healthy option for diabetics and how they can help manage sugar levels.
Understanding Diabetes
Diabetes is a complex condition but there are 3 main types of diabetes: Type 1, Type 2 and gestational.
Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 is usually inherited because you lack the genes to make insulin. Insulin is needed to take glucose (sugars) from the blood and into your cells so your body can use it as energy. Because type 1 diabetics have no ability to produce insulin, they often have to inject insulin so their body can process sugars. Type 1 diabetics often have to have a stricter regime in their diet, testing their sugars and injecting insulin.
Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 is a lifestyle chronic condition where through the years as we grow older, our body becomes insulin resistant. This means our body becomes less efficient in taking in sugars to use as fuel as we age. That is why we commonly see the weight gain, belly bulge, spare tyre around our middle. And even skinny people can get diabetes too! You have seen them before! Those with skinny legs but with a big belly. That is why the waist circumference is the biggest indicator of insulin resistance.
In Type 2 diabetes, your body still produces insulin, but they just don’t work very well. They’re not very efficient in taking the sugars out of the bloodstream and into the cells to use as fuel. That’s why when you go for your blood test, your fasting sugar levels will still be quite high and may be higher than 7.0mmol/L1. So when insulin levels are high, but they’re not very good at taking in sugars into the cell, insulin then tells the body we need to get rid of the sugars and store it as fat. That is why often, there are weight issues associated with type 2 diabetes.
Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes works in the same way as type 2 diabetes, except it only happens during pregnancy. But don’t get lax, as gestational diabetes can lead to increased risk of developing full diabetes later in life in mother and baby2.
How The Ketogenic Diet Works
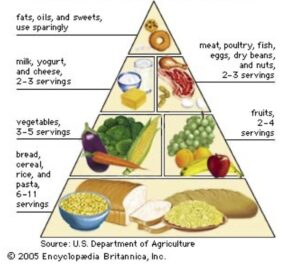
The keto diet is essentially the opposite to the Standard American/Australian Diet (SAD). It is a high fat, low carbohydrate diet. Where SAD uses a lot of processed foods, highly refined grains and meat, low in fresh fruits and vegetables, they are often low in nutrition and high in sugars and carbohydrates. We’ve all seen the typical food pyramid we’ve been taught in school. The photo here is the actual food pyramid developed by the USDA3.
The keto diet aims to change your metabolism from using carbohydrates and sugars as fuel, to using fats as fuel. It focuses on eating healthy fats as your main source of energy. Our aim is to have more fat and protein intake and less carbohydrates and refined sugars, which is great because fats and protein will give your body that ‘full’ feeling. Here is the typical keto diet food pyramid we’ve developed to illustrate this.
So by feeding your body fats, it learns to burn fat. What this means is that you are no longer reliant on sugars as your fuel, so your blood sugars are low and stable and you won’t trigger insulin at all. That means less fat storage by insulin and by doing this, you’re giving your body a break from overworking insulin which eventually leads to less insulin resistance and less of the belly bulge.
The advantage of the keto diet is because it learns to burn fat efficiently, you can burn existing fat stores in your body and it won’t go into starvation mode and reduce metabolism. So you’ll find that you can lose that spare tyre and some can even have significant weight loss when doing the keto diet.
So Is The Keto Diet Good For Diabetics?
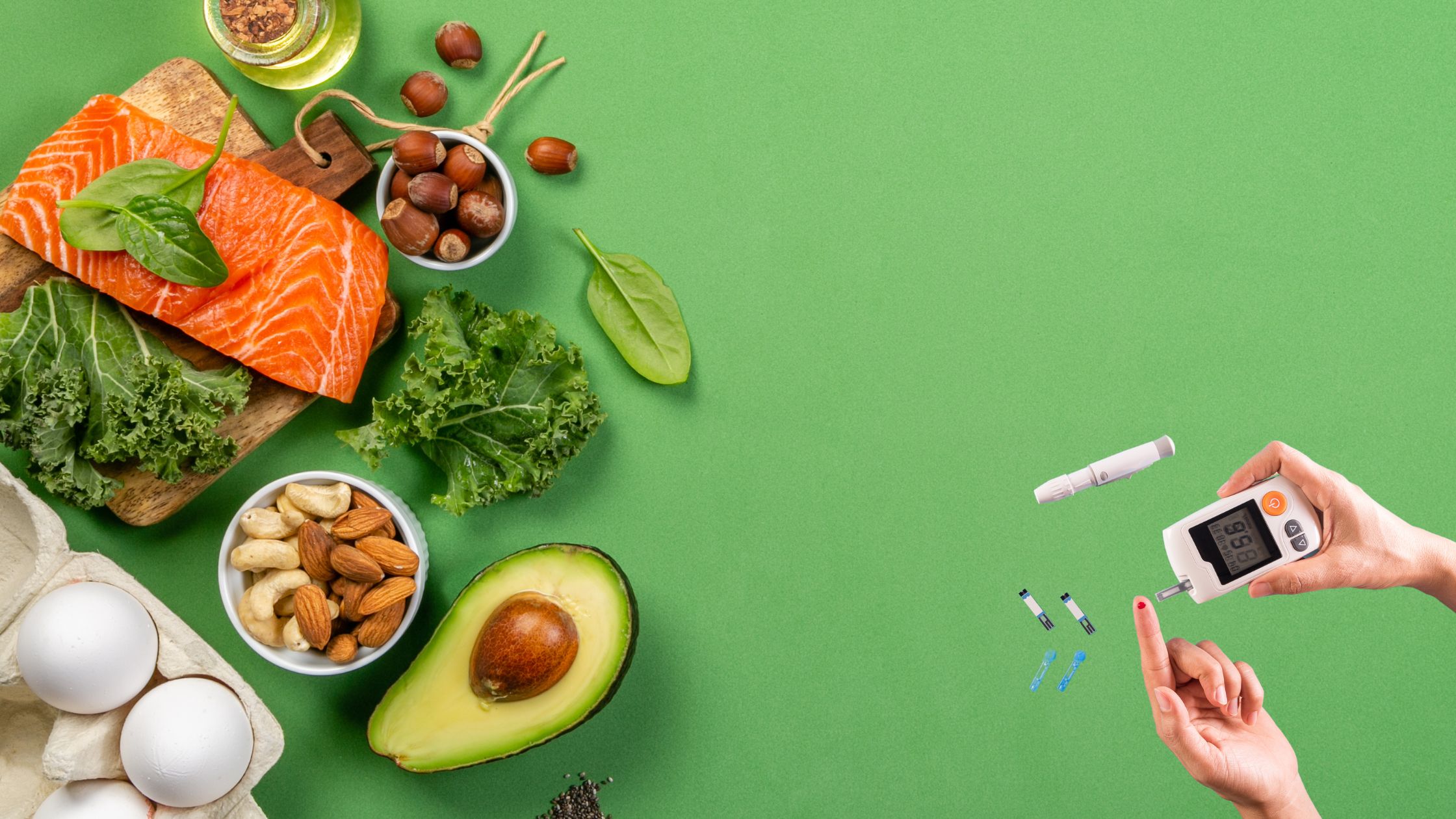
So if keto foods and snacks are formulated to have high fat and low carbs, the low sugar content would naturally not increase blood sugars too much for a diabetic. Low carb snacks will help minimize spikes in blood glucose, right? But wait, that’s not the only thing we have to think about.
You might find that there are quite a few products on the grocery shelf that are marketed as keto. But if you look closely at the ingredient list, you might find some surprises. There may be ingredients in there that you might not know that are actually sugars. For example, there might be starches or hidden sugars such as maltodextrin. Maltodextrin is higher in glycaemic index (GI) than sugar with an index of 185-105 4 and so can increase your blood sugars and trigger insulin. You will often find maltodextrin in many products that claim to be healthy including gluten free, low carb, keto products.
The key to choosing the right keto foods for diabetics is to look for wholefood ingredients and no artificial or hidden sugars. You can try snacks with low GI such as nuts, vegetable sticks, low GI fruits but if you really want to take control of your diabetes and reduce that sugar level and even try to go into remission, a low carb, keto diet is worth considering.
Can My Diabetes Go Into Remission With Keto?
Yes it may! There have been case studies such as this, a 35yr old man who has diabetes, obesity and despite 5 years of being on medications, finally after going on a very low carbohydrate ketogenic diet (VLCKD) managed to lose 20kg with diabetes in remission and even 2 years after follow up, still maintaining his healthy state5. In fact, a low carbohydrate diet can be used in some people to control diabetes. See Dietitians Australia article on how you can go low carb (<130g carbs per day) or very low (20-50g/day) for diabetes management6. So if you’re still wondering ‘Is keto diet good for diabetes?’ the answer is ‘Yes it can!’ As you can see above, there have been people who can come off their medications completely. Most people will likely see improvement in reduction of their medication, better sugar levels and blood results. Of course, the keto diet should be used together with lifestyle improvements such as exercise and checking with your doctor about your medications and constant monitoring. This will mean you get the most chances of success.
What Are Some Healthy Snacks For Diabetics?
Opt for the lower carb snacks like the list below:
- Handful of nuts or seeds
- Hardboiled eggs
- Canned tuna
- Tofu
- Low sugar fruits such as berries
- Full fat, natural yoghurt
- Vegetable sticks
- DIY bake it yourself at home low carb snacks (eg. muffins, cookies, crackers)
Conclusion
If you want to try the ketogenic diet to better manage your diabetes, choose foods with clean, wholesome ingredients and no hidden sugars. Keep Keto snacks, such as our keto crackers and condiments like our sugar free relish and sugar free jam, are suitable for diabetics and the whole family, and made with real whole food ingredients. Visit our shop to explore our full range. Always consult your medical professional and monitor your blood sugar levels, as you might need to adjust your medication when adopting a keto diet. If you have any questions, feel free to reach out and email us.
References
- https://www.racgp.org.au/clinical-resources/clinical-guidelines/key-racgp-guidelines/view-all-racgp-guidelines/diabetes/defining-and-diagnosing-type-2-diabetes
- https://www.diabetesaustralia.com.au/about-diabetes/gestational-diabetes/
- https://www.britannica.com/science/food-pyramid
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/agricultural-and-biological-sciences/maltodextrin#:~:text=Maltodextrin%20has%20a%20high%20glycemic,advice%20of%20a%20healthcare%20practitioner.
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9513631/
- https://dietitiansaustralia.org.au/health-advice/low-carbohydrate-diets-people-type-1-and-type-2-diabetes
- https://idf.org/about-diabetes/diabetes-facts-figures/